
Video
Subject Information
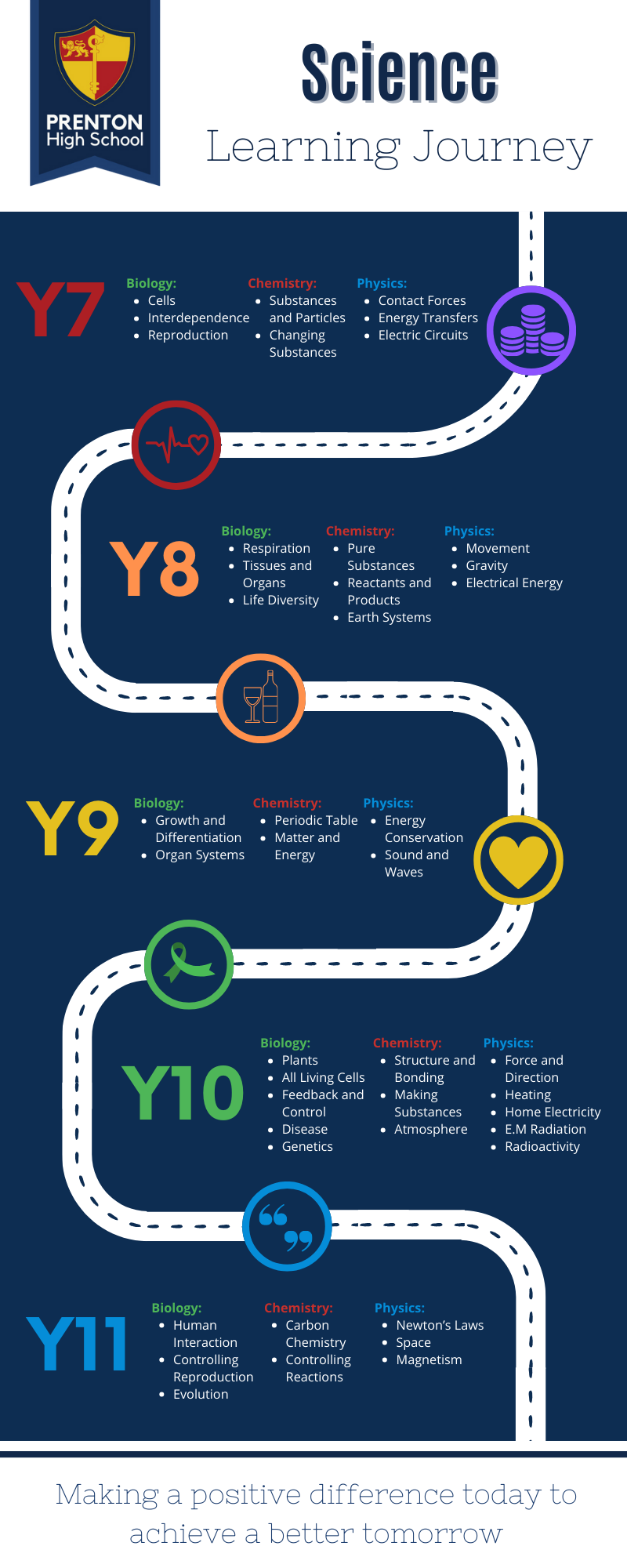
Learning Journey
The aim of KS3 Science at Prenton is to provide the foundations for understanding the world through the disciplines of Biology, Chemistry and Physics. Our lessons are designed to build up a body of key foundational knowledge and concepts, understand how science can be used to explain what is occurring, predict how things will behave and analyse causes.
Our new Year 7 curriculum has been developed in response to the increasing demand of GCSE. Instead of the GCSE exam being largely a knowledge recall test, 60% of the marks are now for transferable understanding (called AO2) and higher level thinking (AO3).
We believe our KS3 curriculum provides a preparation for GCSE assessment objectives AO2 and AO3. It links KS3 to GCSE, helping our students to practice thinking processes, enquiry and maths skills though the application of science. It also supports them to develop a deep understanding of key concepts and the ability to apply them.
From the beginning of secondary science, the KS3 programme covers all of the key concepts and enquiry skills needed to give our students the best possible start and set them up for success in the new, more demanding GCSEs.
Table of Topics
Topics cover five key areas:
- Forces
- Energy
- Matter
- Organisms
- Genes
PHYSICS
| Big Idea | Year 7 | Year 8 | Year 9 |
| Forces predict motion | Forces on materials Balanced & unbalanced forces Friction Density | Movement Speed Motion graphs | See Key Stage 4 |
| Fields produce forces | Gravity Weight Gravitational force Solar system | ||
| Energy is conserved | Energy transfers Heat & Temperature Energy Wasted Energy | ||
| Electricity transfers energy | Electric circuits Electric Current Resistance | Electrical energy Electric charge Voltage | |
| Radiation transfers energy | Light Reflection Refraction |
CHEMISTRY
| Big Idea | Year 7 | Year 8 | Year 9 |
| Structure determines properties | Substances & particles Particle Model Mixtures Solutions | Pure substances Elements & Compounds 8KC-Simple & Giant | See Key Stage 4 |
| Reactions rearrange matter | Changing substances Chemical & Physical pH Scale Neutralisation | Reactants & products Acid reactions Oxidation & reduction | |
| Earth systems interact | Earth systems Earth Processes Potable Water |
BIOLOGY
| Big Idea | Year 7 | Year 8 | Year 9 |
| Cells are alive | Cells Cell Structure Specialised Cells | Respiration Cellular Energy Aerobic & Anaerobic | See Key Stage 4 |
| Bodies are systems | Tissues & organs Cell Organisation Digestive System Gas Exchange | ||
| Organisms are interdependent | Interdependence Feeding Relationships Competition Abiotic & Biotic | ||
| Characteristics are Inherited | Reproduction Sexual & Asexual Menstrual Cycle Embryo Development | ||
| Species show variation | Life diversity Variation Selective Breeding Natural Selection |
Topics at KS4 continue to cover five key areas:
- Forces
- Energy
- Matter
- Organisms
- Genes
PHYSICS
| Big Idea | Year 9 | Year 10 | Year 11 |
| Forces predict motion | Force & direction Force vectors Equilibrium & interactions | Newton’s laws Acceleration Newton’s laws Momentum 11U – Space | |
| Fields produce forces | Magnetism Magnetic field Motor effect | ||
| Energy is conserved | Energy conservation Kinetic & potential Work Energy resources | Heating Thermal transfer Specific & latent Pressure | |
| Electricity transfers energy | Home electricity Power Ohm’s law | ||
| Radiation transfers energy | Sound & waves Wave model Longitudinal & transverse Electromagnetic spectrum | E.M. Radiation Wave behaviour Radioactivity Radioactive decay Half – life |
CHEMISTRY
| Big Idea | Year 9 | Year 10 | Year 11 |
| Structure determines properties | Periodic table Subatomic particles Periodic patterns | Structure & bonding Ionic, covalent, metallic | Carbon chemistry Hydrocarbons Refining |
| Reactions rearrange matter | Matter & energy Atom conservation Reaction energy | Making substances Making salts Amount of substance Electrolysis | Controlling reactions Reaction rate Equilibrium |
| Earth systems interact | Atmosphere Earth’s atmosphere Global warming Product lifecycle |
BIOLOGY
| Big Idea | Year 9 | Year 10 | Year 11 |
| Cells are alive | Growth & differentiation Cell transport Cell division | Plants Photosynthesis Plant transport | |
| Bodies are systems | Organ systems Circulatory system Digestive system Enzymes | Feedback & control Nervous system Endocrine system | |
| Organisms are interdependent | Human interaction Biodiversity Communicable disease System damage Immune system | ||
| Characteristics are inherited | Genetics Genes Monohybrid inheritance | Controlling reproduction Reproductive hormones Genetic engineering | |
| Species show variation | Evolution Evolutionary theory Classification |
GCSE Triple Award (Separate sciences)
Examination board: AQA Biology (8461); Chemistry (8462); Physics (8463)
This qualification is linear meaning that students will sit all examinations at the end of the course. For each GCSE, there are two papers (two Biology, two Chemistry and two Physics). Each of the papers will assess knowledge and understanding from distinct topic areas.
Each of the papers is a written exam: 1 hour 45 minutes (100 marks) worth 50% of each GCSE. Each paper consists of multiple-choice, structured, closed short answer and open response questions. Foundation and Higher Tier. Graded 9-1.
GCSE Science Combined (Trilogy)
Examination board: AQA Trilogy (8464)
This qualification is assessed through examinations at the end of the course. There are six papers; two Biology, two Chemistry and two Physics. Each of the papers will assess knowledge and understanding from distinct topic areas.
Each of the 6 papers is a written exam: 1 hour 15 minutes (70 marks) worth 16.7% of GCSE. Each paper consists of multiple-choice, structured, closed short answer and open response questions. Foundation and Higher Tier. Graded 9-1.
Entry Level Science
Examination board: AQA Entry Level Certificate Science (5960)
Like the GCSE course, this qualification is linear. Linear means that students submit all components that form the assessment at the end of the course. The assessments set are ‘on demand’. This means our students can complete set assignments when they are ready, helping to keep them motivated. The language used in the tests allow students to focus on the science and achieve the results they deserve.
There are two different types of assessment.
- Externally set assignments (ESAs) consist of a short written test. (57%)
- Teacher devised assignments (TDAs) consist of a short piece of practical work. (43%)
Mr P Hignett | Subject Leader – Science | hignettp@prentonhighschool.co.uk

